Continuous Penetration Testing: Key Facts and 5 Reasons Why It’s Critical for Cybersecurity
Table of Contents
What Is Continuous Penetration Testing?
Continuous penetration testing (CPT) is an advanced cybersecurity strategy that involves ongoing and real-time assessments of your systems, networks, and applications. This approach ensures that potential vulnerabilities are identified and mitigated immediately, preventing hackers from exploiting weaknesses that develop over time.
Unlike traditional penetration testing, which is often conducted annually or bi-annually, continuous penetration testing ensures your systems are constantly being evaluated, providing stronger, more reliable security against evolving cyber threats.
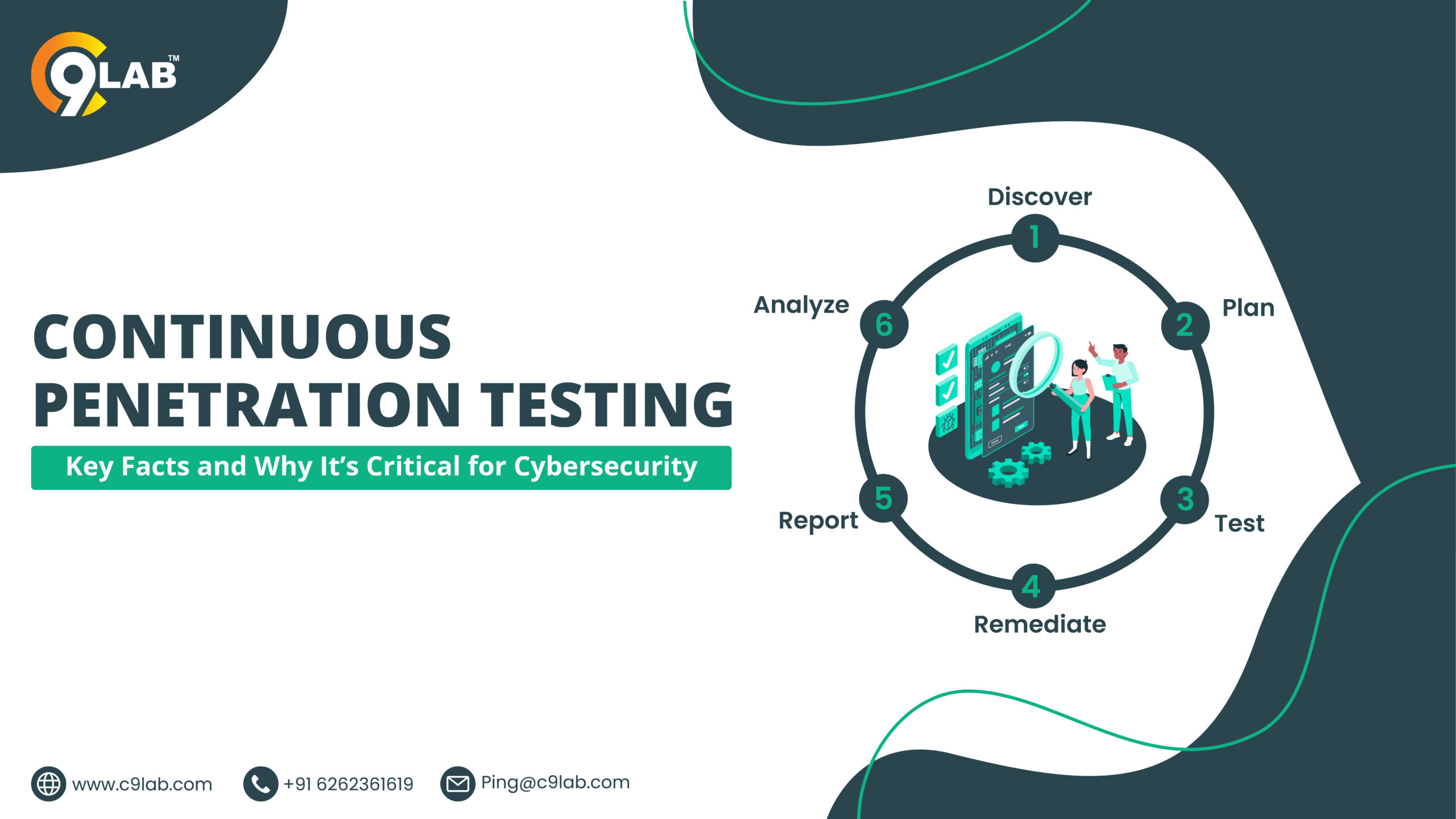
How Continuous Penetration Testing Works
Continuous penetration testing uses a combination of automated tools and manual testing techniques to simulate real-world cyberattacks. This approach helps businesses identify both common and advanced vulnerabilities, offering a comprehensive picture of their security posture.

- Discover – This is the initial phase where potential vulnerabilities are identified across systems, networks, or applications. Automated tools are often employed to scan for weak points that could be exploited by attackers.
- Plan – After discovering vulnerabilities, a strategic plan is created to test these weaknesses. This involves setting up specific attack scenarios to simulate real-world hacking attempts, ensuring that the testing aligns with business goals.
- Test – In this phase, penetration testers (ethical hackers) or automated tools simulate cyberattacks on the discovered vulnerabilities. This helps to evaluate how the system holds up under different attack conditions and pinpoint critical weaknesses.
- Remediate – Once vulnerabilities have been tested, the next step is remediation. This involves fixing or patching the identified vulnerabilities to ensure that attackers cannot exploit them.
- Report – Detailed reports are generated, outlining all discovered vulnerabilities, the methods used to exploit them, and the solutions implemented. These reports help teams understand the current security posture and provide documentation for compliance purposes.
- Analyze – Finally, the analysis phase involves reviewing the results of the penetration test and evaluating how the remediation efforts have improved security. Continuous feedback ensures that the system remains secure over time.
Key elements of continuous penetration testing include:
- Automated Vulnerability Scans: Automated tools continuously scan for known vulnerabilities, misconfigurations, and weaknesses in your systems.
- Manual Pentesting: Ethical hackers, or penetration testers, simulate targeted attacks to identify more complex vulnerabilities that automated systems might miss.
- Real-Time Alerts: Continuous penetration testing provides instant notifications when vulnerabilities are found, allowing for faster remediation and threat management.
Why Continuous Penetration Testing Is Important
The cybersecurity landscape is constantly evolving, and with new vulnerabilities appearing almost daily, companies need a proactive defense strategy. Continuous penetration testing provides that solution by ensuring vulnerabilities are identified and patched as they emerge, rather than waiting for periodic assessments.
Here are some compelling reasons why continuous penetration testing is essential:
1. The Evolving Nature of Cyber Threats
Hackers and cybercriminals are constantly developing new ways to exploit vulnerabilities. Traditional penetration tests, which are performed only once or twice a year, leave long gaps where new threats can go undetected. CPT ensures your systems are always being monitored, reducing the chance of a successful attack.
2. Compliance and Regulatory Requirements
Many industries, especially those handling sensitive information such as financial, healthcare, and e-commerce sectors, must adhere to strict cybersecurity regulations. CPT helps businesses meet ongoing compliance requirements like GDPR, HIPAA, and PCI-DSS, by ensuring their systems are regularly tested and secure.
3. Real-Time Vulnerability Detection
Rather than waiting for a scheduled penetration test to identify weaknesses, continuous penetration testing provides real-time alerts, enabling security teams to address threats as soon as they’re discovered. This immediate feedback drastically reduces the window of opportunity for cybercriminals.
4. Cost Savings in the Long Run
While CPT may seem like an upfront investment, it’s far more cost-effective in the long run. The financial damage from a data breach can be devastating, both in terms of direct financial losses and reputational damage to your business. Early detection and patching of vulnerabilities save you from the heavy costs associated with a cyberattack.
5. Improved Security Awareness
A major benefit of continuous penetration testing is the ability to assess not just technological vulnerabilities but also human weaknesses. This can include testing for phishing attacks or social engineering tactics. By identifying employees who may need additional cybersecurity training, businesses can strengthen their overall security posture.
Continuous vs. Traditional Penetration Testing
To highlight the value of continuous penetration testing, it’s important to compare it with traditional penetration testing. Here’s a breakdown:
| Traditional Penetration Testing | Continuous Penetration Testing |
| Conducted annually or bi-annually | Continuous, real-time vulnerability assessments |
| Focuses on compliance or short-term security | Prioritizes long-term, ongoing security improvements |
| Provides a one-time report after testing | Offers real-time alerts and ongoing vulnerability management |
| Suitable for a snapshot of security at a given time | Ideal for businesses that want ongoing protection from emerging threats |
While traditional penetration testing can be useful for one-time security audits or compliance checks, it lacks the constant monitoring and real-time protection that continuous penetration testing provides.
Technical Aspects of Continuous Penetration Testing
Continuous penetration testing isn’t just about running automated scans—it involves multiple technical layers to ensure comprehensive protection.
1. Automated Vulnerability Scanning
The backbone of CPT is automated vulnerability scanning. Tools such as Nessus, Qualys, or OpenVAS are used to regularly scan systems for weaknesses like unpatched software, misconfigurations, and weak authentication protocols. These scans run at regular intervals and provide immediate reports of any vulnerabilities discovered.
2. Manual Penetration Testing
While automation is a critical part of continuous testing, it’s not sufficient on its own. Manual testing performed by skilled penetration testers adds an additional layer of security. These ethical hackers simulate more sophisticated attack scenarios, such as advanced persistent threats (APTs), which are harder to detect with automated tools.
3. Web Application Security
Web applications are a frequent target for cybercriminals, so CPT also focuses on identifying vulnerabilities specific to web applications, such as SQL injection, cross-site scripting (XSS), and authentication flaws. Tools like Burp Suite and OWASP ZAP are often used for both automated and manual testing of web apps.
4. Network Security Testing
In addition to web applications, continuous testing also covers the overall security of your network infrastructure. This includes identifying open ports, weak encryption protocols, and poorly configured firewalls. A well-segmented network can limit the damage if one area is compromised, which is why this aspect of continuous penetration testing is crucial.
5. Social Engineering Tests
An often overlooked aspect of penetration testing is social engineering. Continuous penetration testing ensures that employees are regularly tested on their security awareness through simulated phishing attacks or other social engineering techniques. This helps to minimize the risk of attacks that exploit human error.
Benefits of Continuous Penetration Testing for Different Industries
Financial Institutions
Financial institutions are prime targets for cybercriminals due to the sensitive nature of their data. CPT helps financial organizations stay compliant with regulations like PCI-DSS and SOX while protecting their customers’ data from unauthorized access.
Healthcare
The healthcare sector handles vast amounts of sensitive data, including personal health information (PHI). Continuous testing helps organizations remain compliant with laws like HIPAA, reducing the risk of data breaches that could expose patient information.
E-commerce
E-commerce platforms handle millions of online transactions daily, making them vulnerable to cyberattacks such as card-not-present fraud, SQL injection, and DDoS attacks. Continuous penetration testing helps secure customer data, maintain PCI compliance, and build trust with online shoppers.
Government Agencies
Government agencies are high-profile targets for nation-state attackers. Continuous penetration testing ensures that potential weaknesses in government networks are identified and patched regularly, safeguarding national security information.
Key Tools for Continuous Penetration Testing
When implementing CPT, businesses have access to a range of tools, both automated and manual, that enhance their cybersecurity posture:
- Nessus: One of the most widely used vulnerability scanners, providing automated detection of security vulnerabilities.
- Qualys: A cloud-based tool for detecting and monitoring vulnerabilities across networks.
- OpenVAS: An open-source vulnerability scanner that offers a comprehensive set of tests for detecting security issues.
- Burp Suite: A web vulnerability scanner commonly used for web application security assessments.
- OWASP ZAP: Another open-source tool designed to identify vulnerabilities in web applications, particularly during the development stage.
By integrating these tools into a continuous testing strategy, businesses can stay proactive in identifying and addressing vulnerabilities as they emerge.
Best Practices for Implementing Continuous Penetration Testing
To maximize the benefits of continuous penetration testing, consider the following best practices:
- Use a Combination of Automated and Manual Tools: While automated vulnerability scanning is essential for day-to-day assessments, manual testing is crucial for detecting advanced threats.
- Monitor in Real-Time: Set up real-time alerts for any vulnerabilities discovered so that your security team can respond quickly.
- Incorporate Testing Into DevOps: By integrating continuous penetration testing into your DevSecOps processes, you can catch vulnerabilities earlier in the development lifecycle.
- Test Both Technology and People: Don’t forget to include social engineering tests to assess your employees’ security awareness.
Conclusion
As cyber threats continue to evolve and become more sophisticated, CPT is becoming a critical element of modern cybersecurity strategies. By providing ongoing assessments, real-time vulnerability detection, and a more robust defense against emerging threats, continuous penetration testing helps businesses stay ahead of cybercriminals and prevent costly breaches.
FAQs About Continuous Penetration Testing
1. How does continuous penetration testing differ from traditional testing?
Traditional penetration testing is done periodically (annually or bi-annually), whereas continuous penetration testing provides ongoing, real-time assessments, detecting vulnerabilities as they appear.
2. What industries benefit the most from continuous penetration testing?
Industries handling sensitive data, such as finance, healthcare, e-commerce, and government agencies, benefit significantly from continuous penetration testing due to strict compliance requirements and the high risk of cyberattacks. These industries need continuous monitoring to maintain a robust security posture and protect sensitive information.
3. What tools are commonly used for continuous penetration testing?
Popular tools include Nessus, Qualys, OpenVAS, Burp Suite, and OWASP ZAP. These tools help automate vulnerability scanning and enable manual testing for deeper insights into potential threats.
4. How often should continuous penetration testing be done?
As the name suggests, continuous penetration testing is an ongoing process. The goal is to continuously monitor, assess, and address vulnerabilities in real-time, ensuring that any new threats are quickly identified and mitigated.
5. Can continuous penetration testing help with compliance?
Yes, continuous penetration testing can help businesses stay compliant with various industry standards and regulations like PCI-DSS, HIPAA, GDPR, and others. Regular testing ensures that companies adhere to security requirements and avoid penalties for non-compliance.
Subscribe to our LinkedIn Newsletter to Stay Updated with Latest Trends and News in Cybersecurity Sphere- Cyber Briefs
