In the world of cybersecurity, social engineering attacks have emerged as one of the most deceptive and dangerous threats. Unlike traditional cyberattacks that rely on technical vulnerabilities, social engineering exploits human psychology to gain unauthorized access to sensitive information or systems. This guide will provide an in-depth look at social engineering attacks, the various types, and how you can protect yourself and your organization from these cunning threats.
Understanding Social Engineering Attacks
Social engineering attacks are manipulative tactics used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into divulging confidential information, such as passwords, financial details, or personal data. These attacks often involve impersonation, deceit, and psychological manipulation, making them particularly challenging to detect and prevent.
Why Are Social Engineering Attacks So Effective?
The success of social engineering attacks lies in their ability to exploit human emotions, such as trust, fear, curiosity, or urgency. Attackers often pose as trusted individuals or entities, convincing their targets to provide sensitive information or perform actions that compromise security. Because these attacks prey on human behavior rather than technical weaknesses, even the most robust security systems can be rendered ineffective if employees or users are not vigilant.
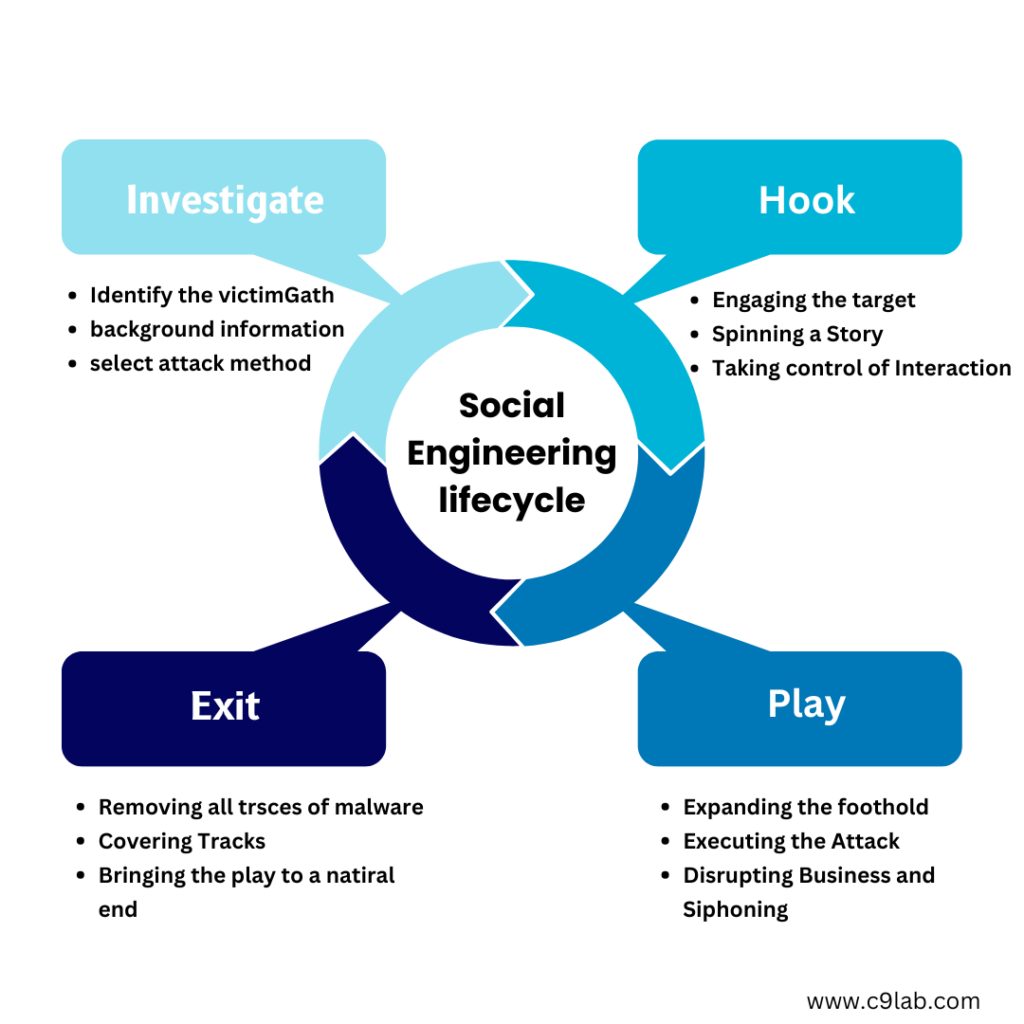
Types of Social Engineering Attacks
Understanding the different types of social engineering attacks is crucial for recognizing and preventing them. Here are some of the most common forms:
1. Phishing
Phishing is the most widespread type of social engineering attack, where attackers send fraudulent emails, messages, or websites that appear legitimate. The goal is to trick recipients into providing sensitive information, such as login credentials, credit card numbers, or personal identification details.
How to Recognize Phishing Attacks:
- Check for suspicious email addresses or domain names that don’t match the legitimate source.
- Be wary of urgent or threatening language designed to create panic or fear.
- Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or untrusted sources.
2. Spear Phishing
Spear phishing is a targeted form of phishing, where the attacker tailors the message to a specific individual or organization. This type of attack is often more convincing because the attacker may use information about the target to appear more credible.
Preventing Spear Phishing:
- Educate employees about the risks and tactics of spear phishing.
- Implement multi-factor authentication (MFA) to add an extra layer of security.
- Regularly update and review security protocols to prevent unauthorized access.
3. Pretexting
Pretexting involves an attacker creating a fabricated scenario or pretext to deceive the target into divulging sensitive information. For example, the attacker might pose as a co-worker, bank official, or IT support personnel to gain the target’s trust.
Tips for Avoiding Pretexting Attacks:
- Verify the identity of anyone requesting sensitive information.
- Use official channels to confirm requests for personal or financial data.
- Train employees to recognize and question unusual requests, even from seemingly trusted sources.
4. Baiting
Baiting involves the use of false promises or offers to lure victims into providing sensitive information or downloading malware. This can include anything from a “free” download of software to physical bait, such as a USB drive left in a public place with a tempting label.
Protecting Against Baiting:
- Educate employees and users about the dangers of unsolicited offers or free downloads.
- Avoid using unknown USB drives or other devices without proper scanning.
- Implement strong network security measures to detect and block malicious downloads.
5. Quid Pro Quo
Quid pro quo attacks involve an attacker offering something of value in exchange for information or access. For example, an attacker might pose as a technical support agent offering free assistance in exchange for login credentials.
Preventing Quid Pro Quo Attacks:
- Be cautious of unsolicited offers of help, especially if they require providing sensitive information.
- Always verify the identity and legitimacy of anyone requesting information.
- Educate employees about the risks of exchanging information for services or favors.
6. Tailgating (Piggybacking)
Tailgating, also known as piggybacking, is a physical social engineering tactic where an unauthorized person gains access to a secure area by following an authorized individual closely. This often occurs in workplaces with controlled access points.
How to Prevent Tailgating:
- Implement strict access control policies and ensure employees are trained to follow them.
- Use security measures such as ID badges, access cards, and security personnel to monitor entry points.
- Encourage employees to report any suspicious behavior immediately.
Best Practices for Preventing Social Engineering Attacks
Preventing social engineering attacks requires a combination of awareness, training, and security measures. Here are some best practices to protect yourself and your organization:
1. Regular Security Training
Conduct regular training sessions to educate employees about the different types of social engineering attacks and how to recognize them. Use real-world examples and phishing simulations to reinforce learning.
2. Implement Multi-Factor Authentication (MFA)
MFA adds an additional layer of security by requiring users to verify their identity through multiple methods before gaining access to sensitive systems or information. This can help prevent unauthorized access, even if login credentials are compromised.
3. Establish Clear Security Policies
Develop and enforce clear security policies that outline the proper handling of sensitive information, email protocols, and access control measures. Ensure that employees understand the importance of following these policies to prevent security breaches.
4. Encourage a Culture of Caution
Encourage employees to be cautious and skeptical of unexpected requests for information, even if they appear to come from a trusted source. Reinforce the idea that it’s better to verify the legitimacy of a request than to risk a security breach.
5. Use Advanced Security Solutions
Leverage advanced security solutions like C9Lab’s C9Phish, which provides AI-powered phishing mitigation, and C9Eye, which offers comprehensive monitoring and alerts for suspicious activities. These tools can help detect and prevent social engineering attacks before they cause harm.
Conclusion
Social engineering attacks are a serious threat to both individuals and organizations. By understanding the various types of attacks and implementing the best practices outlined in this guide, you can significantly reduce your risk of falling victim to these deceptive tactics. Staying informed, vigilant, and proactive is key to protecting yourself and your organization from the ever-evolving landscape of cyber threats.
FAQs
1. What is a social engineering attack?
A social engineering attack is a manipulative tactic used by cybercriminals to trick individuals into divulging confidential information or performing actions that compromise security.
2. How can I recognize a phishing attack?
Phishing attacks often involve suspicious email addresses, urgent language, and requests for sensitive information. Avoid clicking on links or downloading attachments from unknown or untrusted sources.
3. What is the difference between phishing and spear phishing?
Phishing is a broad attack targeting many individuals, while spear phishing is a targeted attack aimed at a specific individual or organization, often using personalized information.
4. How can I prevent pretexting attacks?
Verify the identity of anyone requesting sensitive information, use official channels to confirm requests, and train employees to recognize unusual requests.
5. What role does C9Lab play in preventing social engineering attacks?
C9Lab offers advanced security solutions, including AI-powered phishing mitigation and comprehensive monitoring tools, to help detect and prevent social engineering attacks.
Keep your business safe and informed with the latest cybersecurity news, insights, and expert tips.
📬 Subscribe to Our Newsletter: Cyber Briefs
